Medicinal Plants of Odisha
-
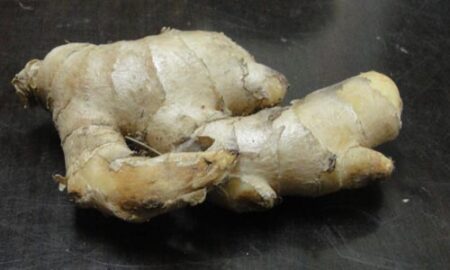
Ada
Botanical name: Zingiber officinale Family: Zingiberaceae Local name: Ada, Adrak Common name: Ginger Parts used: Rhizome Plant character: It is an herbaceous, rhizomatous, perennial plant with thick aromatic edible rhizome. The leaves are long and lanceolate. It prefers partial shade. It is widely cultivated as a spice crop. USES:
Around the world, Ginger is used as a spice and condiment. It is a key ingredient in Indian cooking and used as a medicine for indigestion and migraine.
-
Agasthi
Botanical name: Sesbania grandiflora Family: Fabaceae Local name: Agasthi Common name: Vegetable Hummingbird Parts used: Flower Plant character: It is a small leguminous and fast-growing tree with compound leaves and large white, red or pink flowers. Pods are elongated and drooping. Plant grows under adequate sunlight but can be grown in semi-shade condition. It is mostly grown as an ornamental and economic plant. USES:
Sesbania grandiflora flowers are used as a medicine to cure night blindness, chronic cough, swelling, sprains, dysentery and malaria.
-
Amarpoi
Botanical name: Kalanchoe pinnata
(=Bryophyllum pinnatum)Family: Crassulaceae Local name: Amarpoi, Patragaja Common name: Air plant/ Miracle plant/ Life plant Parts used: Leaves Plant character: It is a succulent perennial plant with fleshy leaves. It can survive in low light but grows best in full sun or bright indirect light. It can be cultivated in kitchen garden. USES:
This plant is also known as miracle plant and leaves of this plant used for the treatment of diarrhoea, piles, diabetes, liver damages, urinary problems, respiratory infections, applied to wounds and insect bites.
-
Ambiliti
Botanical name: Oxalis corniculata Family: Oxalidaceae Local name: Ambiliti, Kumari Common name: Yellow wood sorrel Parts used: Leaf Plant character: Annual trailing hairy herb with creeping stems, rooting at nodes. Leaves trifoliolate, palmate. Flowers are yellow. It thrives well in partial shade. Wild in shady moist localities, dilapidated walls and buildings, but can be cultivated. USES:
Leaf decoction is used in fever and dysentery. Leaves are edible as a vegetable.
-
Amla
Botanical name: Phyllanthus emblica
(=Emblica officinalis)Family: Euphorbiaceae Local name: Amla, Aonla Common name: Indian Gooseberry Parts used: Fruits Plant character: Small of medium-sized tree. Mostly wild in forests, also planted and cultivated. Flowers creamish-white, fruit round, ribbed. Plant is a light demander. USES:
The fruits are a rich source of vitamin C. Fruits are eaten raw and cooked as well. Both dried and fresh fruits are used in Indian traditional medicine. Amla is beneficial for hair growth, skin, cold, cough and intestinal health.
-
Amrutabhanda
Botanical name: Carica papaya Family: Caricaceae Local name: Amrutabhanda, Papaya Common name: Tree Melon Parts used: Fruits, Latex, leaf Plant character: It is an unbranched laticiferous tree with fistular stem and large, palmate, long-petioled leaves. Fruits are obovate, yellow/orange when ripe. Seeds round, black. Grow best in full sun. It is a widely cultivated plant. USES:
People use green papaya for cooking. Plants are beneficial for cancer, diabetes, dengue and fever. Ripe fruits are used to prevent night blindness.
-
Ankaranti
Botanical name: Solanum virginianum
(Syn. Solanum surattense, S. xanthocarpum)Family: Solanaceae Local name: Ankaranti, Kanta Kari Common name: Suratlense Nightshade Parts used: Seeds, Fruits Plant character: It is a spreading herb with prominent yellow spines, blue-purple flowers. Fruits are globose with prominent nerves. Wild in sandy localities, waste places; can be cultivated. The fruits are edible. USES:
Powder of seeds is smoked in a pipe to get rid of worms in dental caries. Decoction of whole plant is used in control of urinary problems.
-
Aparajita
Botanical name: Clitoria ternatea Family: Fabaceae Local name: Aparajita Common name: Butterfly pea Parts used: Leaf, Root Plant character: It is a slender climbing legume with hairy branches and compound leaves. Flowers are blue of white. Pods are compressed, many-seeded. The flowers are large and ornamental. It is wild in forests, village hedges and thickets; also grown in gardens. The plant prefers full sun for best growth. USES:
Aparajita is a holy flower in India. Leaf extract is used to make a person recover from unconscious stage. Plant is also used to cure face pimples.
-
Arakha
Botanical name: Calotropis gigantea Family: Asclepiadaceae Local name: Arakha, Arka Common name: Crown flower, Giant Milkweed Parts used: Leaf, Milky latex Plant character: It is an erect shrub with milky latex, covered with white, cottony hairs. Flowers are pale-purple, fleshy. Fruits horn-shaped, fleshy. It prefers full sunlight. The plant grows wild along roads, in waste places, sandy localities; but can also be cultivated. USES:
The milky latex of the plant is applied to relieve pain due to migraine. Dry flower with ghee is taken to cure asthma. Warm leaves with oil are applied in inflamed parts of the body. Ash of leaves is used with honey to cure asthma and bronchitis.
-
Arjuna
Botanical name: Terminalia Arjuna Family: Combretaceae Local name: Arjuna Common name: Arjun Parts used: Stem bark Plant character: It is a large deciduous tree with spreading crown, drooping branches and smooth flaking bark. The flowers are yellowish-white; fruits are large and winged. Wild along streams, rivers and other mopist localities. It prefers bright sunlight. USES:
Terminalia arjuna is an important cardiotonic plant described in the Ayurveda, the ancient Indian medical science. It is also believed to have the ability to cure hepatic, urogenital, venereal and viral diseases. The bark of the plant has several medicinal properties.
-
Asoka
Botanical name: Saraca asoca
(=Saraca indica)Family: Fabaceae Local name: Asoka Common name: Ashoka/ sorrowless tree Parts used: Bark Plant character: Small ever-green tree with large compound leaves, red/yellow or pink fragrant flowers in large clusters. Young leaves are colourful and drooping in nature. Fruits are large, semi-cylindrical with large seeds. It prefers shady moist localities for better growth and flowering. It is a wild along streams, also grown as an ornamental plant. USES:
Stem bark is useful in dyspepsia, fever, pain and inflammation. It also cures leucorrhoea and metrorrhoea.
-
Aswagandha
Botanical name: Withania somnifera Family: Solanaceae Local name: Aswagandha Common name: Indian ginseng/winter cherry Parts used: Root, Leaf Plant character: It is a perennial herb or sub-shrub, branches extending radially from a central stem. Flowers are yellowish-green; fruits orange to red, encapsulated in an inflated calyx. It prefers a warm sheltered position in full sun. This plant grows gregariously in suitable habitats in the wild and are also cultivated. USES:
Root powder is useful as a tonic and for anemia and insomnia. Tea prepared from leaf is taken for curing cold and cough.
-
Aswastha
Botanical name: Ficus religiosa Family: Moraceae Local name: Aswastha, Osta Common name: Sacred fig, Pipal Parts used: Latex, Leaf, Bark Plant character: It is a large deciduous tree with milky latex, ovate, acuminate leaves and small red-colour syconia (fruits). It prefers bright direct sunlight, can tolerate partial indirect light. It is found in the wild; also planted. USES:
Ficus religiosa is a sacred tree among followers of Hinduism, Jainism and Buddhism. Traditionally it is used against diabetes, asthma, nasal bleeding, burning, gastric problems and in sexual disorders.
-
Bacha
Botanical name: Acorus calamus Family: Iridaceae Local name: Bacha, Bach Common name: Sweet flag, Muskrat root Parts used: Rhizome Plant character: It is an erect perennial herb with grass-like leaves and hard aromatic rhizomes. Leaves are flesy. It thrivesin full sun and part shade but under moist situations. This plant is found both in wild and cultivated conditions. USES:
It has been used medicinally for a wide variety of ailments, such as gastrointestinal diseases and treating pain, as a sedative, analgesic. It is also used in epilepsy and hypertension. Rhizome used for clearing throat and throat infection.
-
Bahada
Botanical name: Terminalia bellirica Family: Combretaceae Local name: Bahada, Bahera Common name: Bastard myrobalan, Beleric Parts used: Bark, Fruits, Seeds Plant character: It is a large deciduous tree with yellowish-white flowers and ovate ridged fruits. It prefers sunlight and cannot grow in the shade. The fruits are widely collected for use an ingredient of Ayurvedic drug “Triphala”. Though wild in the forests, can be grown in open space. USES:
Plant is used to enhance digestion, and boost immunity. Seeds and fruits are beneficial for curing asthma, cough and blood vomiting.
-
Bara
Botanical name: Ficus benghalensis Family: Moraceae Local name: Bara Common name: Banyan tree Parts used: Bark, fruits Plant character: It is a gigantic tree with spreading crown and prominent prop roots. This tree prefers plenty of bright sunlight. Wild in forests and in village groves, usually worshipped and grown in courtyards having plenty of space. USES:
This plant is useful in skin diseases, inflammation and toothache. It is also beneficial for controlling diabetes and vitality in males. Fruits are beneficial for controlling leprosy, nasal bleeding.